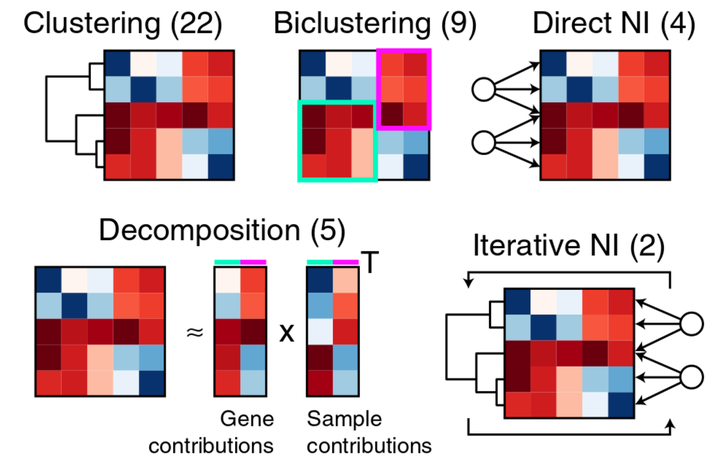
 Different types of module detection methods included in the evaluation.
Different types of module detection methods included in the evaluation.Abstract
A critical step in the analysis of large genome-wide gene expression datasets is the use of module detection methods to group genes into co-expression modules. Because of limitations of classical clustering methods, numerous alternative module detection methods have been proposed, which improve upon clustering by handling co-expression in only a subset of samples, modelling the regulatory network, and/or allowing overlap between modules. In this study we use known regulatory networks to do a comprehensive and robust evaluation of these different methods. Overall, decomposition methods outperform all other strategies, while we do not find a clear advantage of biclustering and network inference-based approaches on large gene expression datasets. Using our evaluation workflow, we also investigate several practical aspects of module detection, such as parameter estimation and the use of alternative similarity measures, and conclude with recommendations for the further development of these methods.